The Windows Kernel-Power 41 error is one of the most common system issues faced by Windows users. If you’ve ever experienced your PC suddenly restarting or shutting down without warning, only to find “Kernel-Power Event ID 41” in the Event Viewer, you’re not alone.
This error doesn’t always point to one single cause, which makes it frustrating. However, with the right troubleshooting steps, you can fix Kernel Power 41 and prevent unexpected system crashes.
In this article, we’ll explain what the error means, why it happens, and how to resolve it effectively.
What is the Kernel Power 41 Error?
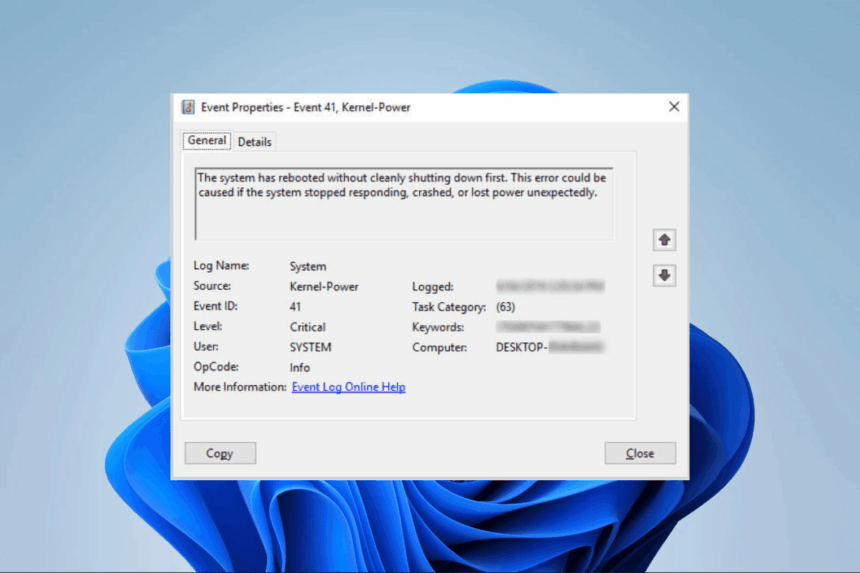
The Kernel-Power 41 error occurs when Windows detects that your system was shut down unexpectedly. It usually appears in the Event Viewer under the System logs with Event ID 41 (Critical).
In simple terms, it means your PC either:
- Lost power abruptly.
- Restarted without a clean shutdown.
- Encountered a hardware or driver issue that forced it to stop.
While the error itself doesn’t specify the exact cause, it’s a sign that something isn’t working as it should.
Common Causes of Windows Kernel Power 41
Before fixing the issue, it’s important to understand what might be causing it. The most common reasons include:
- Faulty Power Supply Unit (PSU) or sudden power loss.
- Overheating CPU or GPU leading to forced shutdowns.
- Outdated or corrupt drivers, especially graphics and chipset drivers.
- BIOS misconfigurations or outdated firmware.
- Overclocking issues affecting system stability.
- Faulty RAM or hardware components.
- Improper Windows power settings.
Since multiple factors can trigger it, the fix often involves a mix of hardware checks and software adjustments.
1. Check Your Power Supply and Hardware
The first step in resolving the Kernel Power 41 error is ensuring your system is not facing physical issues.
- Make sure your power cables are properly connected.
- If you’re on a desktop, verify that the PSU (Power Supply Unit) is sufficient for your hardware. Weak or failing PSUs are one of the leading causes of this error.
- Clean dust from your system to avoid overheating.
- Use monitoring tools like HWMonitor or MSI Afterburner to check CPU and GPU temperatures.
If your PC is overheating, clean the fans, reapply thermal paste, or improve airflow inside your case.
2. Update Windows and Device Drivers
Outdated or corrupt drivers can trigger system instability. To fix this:
- Press Win + I to open Settings.
- Go to Update & Security → Windows Update.
- Install all pending updates.
- For drivers, open Device Manager (Win + X → Device Manager).
- Right-click your GPU, network adapter, and chipset → Update driver.
Alternatively, visit your manufacturer’s website (NVIDIA, AMD, Intel, etc.) to download the latest drivers.
3. Change Windows Power Settings
Incorrect power settings can also cause sudden shutdowns. Adjusting them may prevent the Kernel Power 41 crash.
- Open Control Panel → Power Options.
- Select High Performance as your power plan.
- Click Change plan settings → Change advanced power settings.
- Expand Hard Disk → Set Turn off hard disk after to Never.
- Expand Sleep → Disable Hibernate after and Allow hybrid sleep.
This ensures your system doesn’t go into unstable power states.
4. Disable Overclocking
If you’ve overclocked your CPU, GPU, or RAM, the Kernel Power 41 error may appear when your system becomes unstable.
- Enter the BIOS/UEFI (usually by pressing DEL or F2 during boot).
- Reset all overclocked settings to default.
- Save and exit.
Running hardware at factory settings often resolves the issue.
5. Check and Repair System Files
Corrupted system files can also lead to critical errors. Running Windows repair tools may fix the problem.
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator.
- Type the following command and press Enter:
sfc /scannow - Wait for the scan to finish and repair files.
- Next, run:
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth
This ensures your system files and image are not corrupted.
6. Update BIOS/UEFI
An outdated BIOS can sometimes cause Kernel Power 41 issues, especially with modern CPUs.
- Check your motherboard manufacturer’s website for the latest BIOS version.
- Follow their official instructions carefully to update.
Caution: Updating BIOS carries some risk. Make sure your system doesn’t lose power during the update.
7. Test Your RAM and Hardware
Faulty RAM or storage can also trigger unexpected shutdowns.
- Run Windows Memory Diagnostic (search it from the Start menu).
- Use tools like MemTest86 for deeper memory checks.
- Check your SSD/HDD with CrystalDiskInfo for potential failures.
If errors are found, replacing the faulty component may be necessary.
The Windows Kernel Power 41 error can be tricky because it’s more of a symptom than a direct cause. It simply tells you that Windows wasn’t shut down properly. The real issue could be power, drivers, overheating, or even faulty hardware.
For most users, starting with power supply checks, updating drivers, and adjusting power settings solves the issue. If the error persists, more advanced troubleshooting, like BIOS updates or hardware testing, may be required.
- Microsoft Enhances Kernel Security Post-CrowdStrike
- Most Used Operating Systems in the World
- Fix the Second Monitor lagging in Windows 11