Although there are many spreadsheet management and creation tools available, Microsoft Excel remains the preferred choice for millions of users across professional, academic, and personal settings. It’s one of the most powerful and versatile applications in Microsoft’s Office suite.
However, despite its popularity, Excel has had its fair share of limitations-one of the most notable being the manual updating of PivotTables (dynamic tables).
Microsoft Excel’s most recent update corrects an important problem with dynamic tables
Microsoft has recently addressed this issue in an important update to Excel, as confirmed by How-To Geek. The update solves a long-standing problem that required users to manually refresh data in PivotTables when changes were made to the source data. Now, PivotTables will update automatically when modifications occur in the data range-eliminating a tedious step and improving workflow efficiency.
This improvement is part of an Excel update that will roll out automatically for both Windows and macOS users.
In a blog post, Microsoft acknowledged that PivotTables are a key feature for summarizing, calculating, and analyzing large datasets, but users had consistently expressed frustration over the need for manual updates. With this update, automatic refreshing will become the default behavior for new PivotTables.
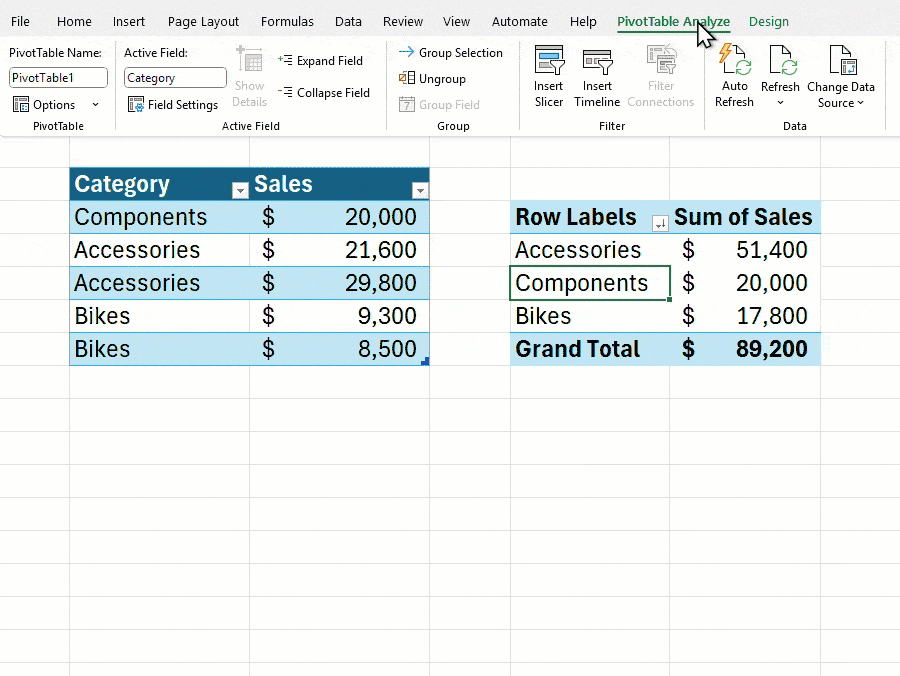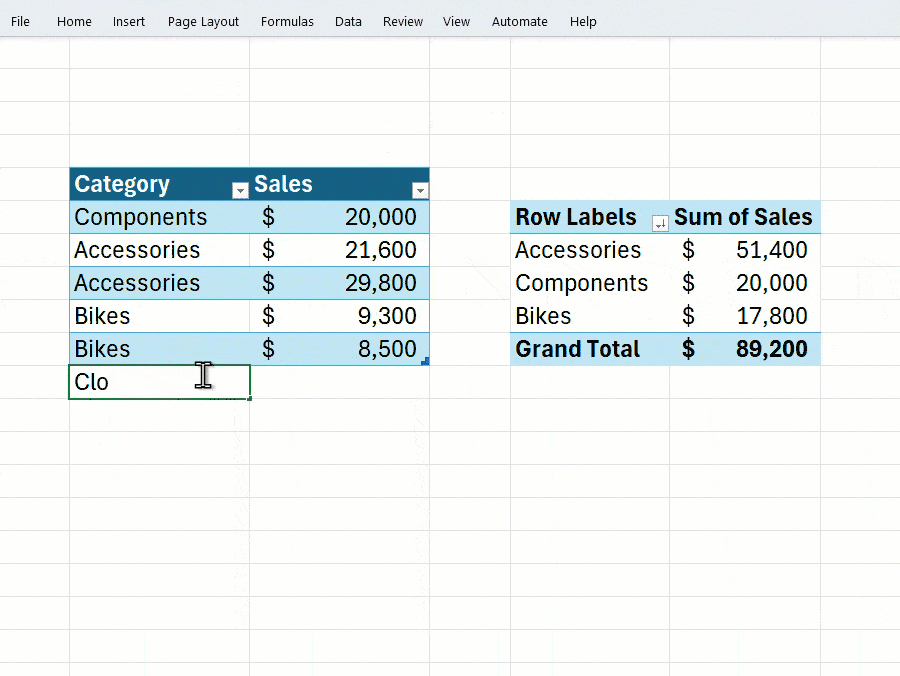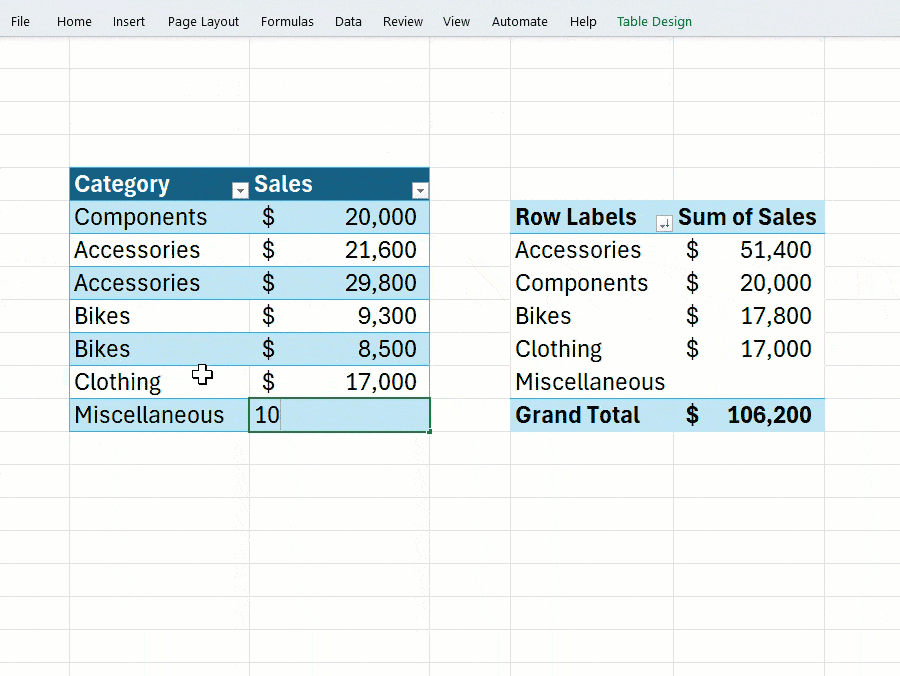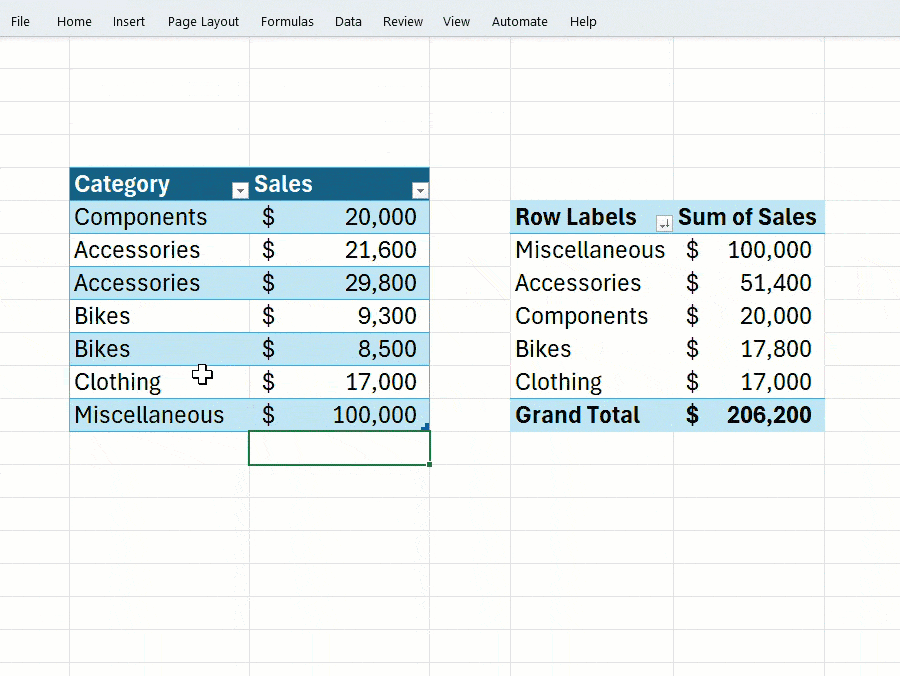
Users will find the option to toggle this setting in the PivotTable Analyze tab under a new “Auto Update” option. However, there are some limitations: this feature currently only works with data from the current workbook–external or asynchronous sources are not supported. Additionally, if you’re collaborating with others using older versions of Excel, some compatibility issues may arise.
If the automatic update fails to activate, or if it is disabled, Excel will display an indicator in the bottom-left corner of the window to notify users that one or more PivotTables may be using outdated data.
While questions remain about how this feature will perform with extremely large datasets, it’s a significant quality-of-life improvement. The update is currently available on the Microsoft 365 Beta Channel for users running version 2506 (Build 19008.2000 or later) on Windows. A rollout to the stable version is expected in the near future.
Overall, this update shows that Microsoft is actively listening to user feedback and improving Excel in ways that enhance productivity and usability.