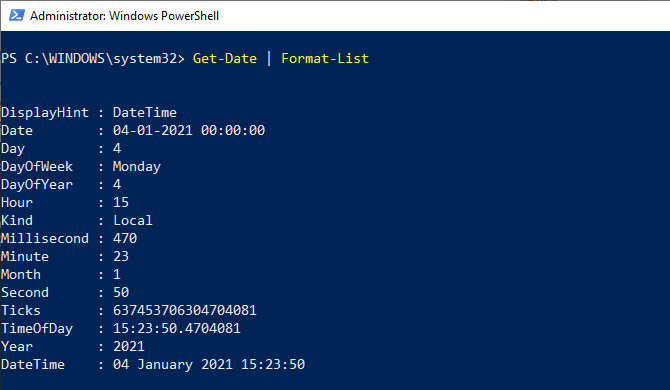
Managing cloud environments such as Microsoft 365 and Azure Active Directory can quickly become time-consuming if you rely solely on graphical admin portals. For administrators who want speed, consistency, and scale, automation is essential. That’s where the Microsoft Graph PowerShell module becomes an incredibly valuable tool, giving IT teams direct, scriptable access to Microsoft’s cloud ecosystem.
What is Microsoft Graph PowerShell?
Microsoft Graph PowerShell is a command-line module that allows administrators to interact with Microsoft cloud services using PowerShell. Instead of clicking through multiple admin panels, you can manage users, groups, licenses, devices, calendars, files, and security settings using simple, repeatable commands.
Because it’s built on Microsoft Graph, the module provides a single, unified way to access data across Microsoft services. This makes it especially useful for automation tasks such as bulk user management, reporting, onboarding and offboarding workflows, and scheduled maintenance jobs. For anyone already comfortable with PowerShell, the learning curve is minimal.
Another major advantage is consistency. Scripts written with Microsoft Graph PowerShell behave consistently, reducing human error and making large-scale administration far more reliable than manual changes.
Why use Microsoft Graph PowerShell?
For IT professionals and system administrators, the module offers several practical benefits:
- Automates repetitive administrative tasks
- Simplifies bulk operations across Microsoft 365 services
- Provides deeper control than some web-based admin portals
- Makes it easier to document and audit administrative actions
- Integrates smoothly with existing PowerShell scripts and workflows
Whether you’re managing a small tenant or a large enterprise environment, Microsoft Graph PowerShell helps you work faster while maintaining consistency and control.
System requirements for Microsoft Graph PowerShell
Before installing the module, confirm that your system meets the basic prerequisites. These ensure compatibility and prevent common installation issues.
You’ll need the following:
- PowerShell version 5.1 or newer is installed on your system
- .NET Framework 4.7.2 or later
- An up-to-date version of PowerShellGet
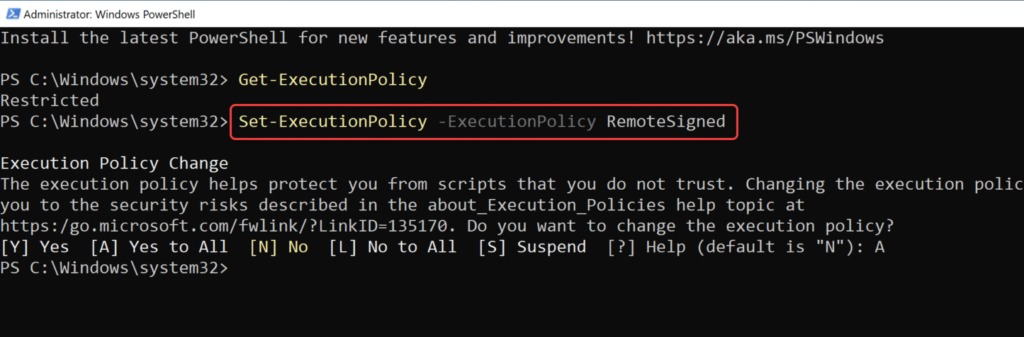
- A script execution policy set to RemoteSigned or a less restrictive setting
These requirements apply to most modern Windows systems, so many users will already be ready to go without additional setup.
Getting ready for installation
Once your environment meets the requirements, installing Microsoft Graph PowerShell is straightforward. After installation, you can connect to your Microsoft 365 tenant, grant the required permissions, and begin managing resources immediately through the command line.
For administrators looking to streamline daily tasks and reduce reliance on manual configuration, Microsoft Graph PowerShell isn’t just a convenience—it’s quickly becoming a necessity.
To update your execution policy (if needed), run:
Set-ExecutionPolicy -ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Scope CurrentUser
Installing Microsoft Graph PowerShell Module
1. Start by opening PowerShell with administrator privileges. Right-click the PowerShell icon and select “Run as administrator” from the context menu.
2. With PowerShell running, execute this command to fetch and install the module:
Install-Module Microsoft.Graph -Scope CurrentUser
3. When prompted about installing from an untrusted repository, type Y and press Enter to continue. The system will download and install the necessary components.
4. Once the installation finishes, check that everything is installed correctly by running:
Get-InstalledModule Microsoft.Graph
You’ll see details about the module version, name, and description if the request is successful.
Working with Microsoft Graph PowerShell
Importing the Graph Module
Before using any Microsoft Graph commands in a new PowerShell session, you’ll need to import the module:
Import-Module Microsoft.Graph
Connecting to Microsoft Graph
To start working with Microsoft 365 resources, you’ll need to authenticate. The following command connects to Microsoft Graph with specific permission scopes:
Connect-MgGraph -Scopes "User.Read.All","Group.ReadWrite.All"
This will trigger an authentication dialog. If your account has Multi-Factor Authentication enabled, you must complete the verification process using your authentication app.
After successful authentication, PowerShell will display a welcome message confirming your connection.
Running Your First Command
With everything set up, you can now start managing your Microsoft 365 environment. For example, to list all users in your organisation:
Get-MgUser -All
Maintaining Your Installation
Updating the PowerShell Graph Module
Keep your Microsoft Graph PowerShell module up to date by running:
Update-Module Microsoft.Graph
Uninstalling the Graph Module
If you need to remove the module completely, run these commands in sequence:
Uninstall-Module Microsoft.Graph -AllVersions
Get-InstalledModule Microsoft.Graph.* | ? Name -ne "Microsoft.Graph.Authentication" | Uninstall-Module
Uninstall-Module Microsoft.Graph.Authentication
The Microsoft Graph PowerShell module transforms how IT professionals interact with Microsoft 365 services. Instead of clicking through admin portals, you can now script and automate your administrative tasks, saving valuable time while reducing human error.
Whether you’re managing hundreds of user accounts, configuring security settings, or just pulling reports on your environment, this tool puts the full power of Microsoft Graph at your fingertips through familiar PowerShell commands.
As your organisation’s cloud footprint grows, mastering tools like Microsoft Graph PowerShell becomes increasingly valuable, allowing you to build sophisticated management solutions that would be impossible through conventional interfaces.
Now that you’ve installed and configured the module, you’re ready to explore the hundreds of cmdlets available to manage your Microsoft cloud environment more effectively than ever before.