Researchers at Aikido Security have uncovered a significant new vulnerability pattern that threatens the foundations of how modern software is built.
The flaw—named PromptPwnd—reveals how AI prompt injection can be used to compromise automated development pipelines such as GitHub Actions and GitLab CI/CD, especially when organisations integrate AI agents like Gemini, Claude Code, and OpenAI Codex into those workflows.
This marks one of the first confirmed cases where AI-driven automation has directly exposed major firms to real, reproducible supply-chain attacks.
Why AI Automation Has Become a New Security Risk
Many companies now rely on AI inside their CI/CD processes to automate tasks such as:
- classifying bug reports,
- generating code suggestions,
- triaging issues, and
- managing development tasks.
PromptPwnd shows how fragile this automation becomes when AI systems interact with untrusted text—for example, when an AI agent reads a bug report title submitted by an outsider.
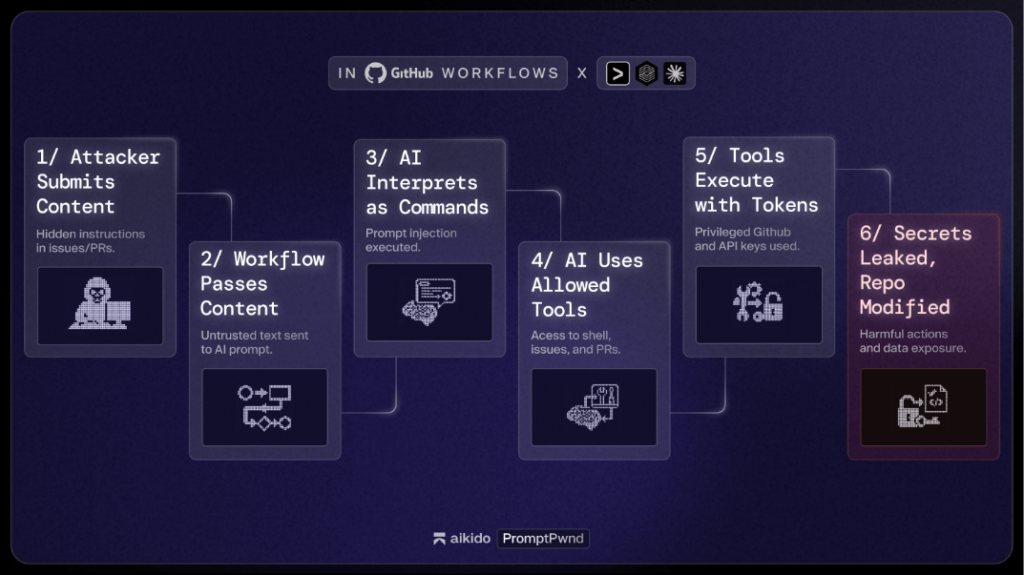
How the attack works:
- An attacker embeds hidden instructions in the text (a classic prompt injection).
- The AI agent processes that text and mistakenly treats the attacker’s message as a legitimate command.
- The AI then uses its privileged access inside the CI/CD pipeline to run tools or extract secrets.
- This can lead to theft of security tokens, modification of workflows, or full takeover of the build environment.
This attack vector is particularly concerning because it bypasses traditional code review or permission barriers. The AI effectively becomes the attacker’s bridge into restricted automation systems.
Aikido Security notes that this weakness resembles earlier software-supply-chain attacks—such as Shai-Hulud 2.0—that targeted CI/CD ecosystems, but PromptPwnd is unique in showing how AI itself can become an unexpected execution surface.
Exposure Confirmed in Multiple Fortune 500 Companies
Aikido researchers verified the vulnerability in at least five Fortune 500 organisations, confirming the attack pattern was not hypothetical but active and exploitable in real workflows.
Their findings were summarised as:
- “Practical, reproducible, and already present in real-world GitHub Actions.”
One of the highest-profile exposures involved Google’s Gemini CLI repository, where the PromptPwnd chain could be triggered. After the issue was privately disclosed, Google patched the flaw within four days.
This represents one of the first concrete proofs that AI prompt injection can compromise critical software pipelines, not just generate incorrect output or misleading responses.
Other AI Tools Affected: Claude Code, OpenAI Codex, and More
PromptPwnd is not isolated to a single product. Similar weaknesses were identified in:
- Claude Code Actions
- OpenAI Codex Actions
- Various community-built AI GitHub Actions
These tools include safety mechanisms requiring explicit user permissions. However, many organisations unknowingly disable these protections through configuration options, leaving pipelines vulnerable.
One of the most serious risks highlighted is theft of the GITHUB_TOKEN, a credential that can grant attackers the ability to:
- push malicious code,
- open supply-chain backdoors,
- alter build scripts, or
- manipulate release artifacts.
Industry Response: Open-Source Rules and Mitigation
Aikido Security has open-sourced a set of Opengrep rules to help organisations detect vulnerable patterns in their own codebases. These rules are designed to identify places where untrusted text flows directly into AI prompts—something traditional static-analysis tools do not detect.
Recommended Immediate Defenses:
- Restrict tool permissions for AI agents inside CI/CD pipelines.
- Never pass untrusted user input directly into AI prompts used in automation.
- Re-enable safety permissions that prevent AI agents from executing privileged actions.
- Audit all GitHub Actions and GitLab CI/CD steps where AI is given access to security tokens or repository write permissions.
Security teams warn that organisations rushing to integrate AI into development workflows may unintentionally expand their attack surface unless they adopt stricter controls and treat AI prompts as executable code pathways.