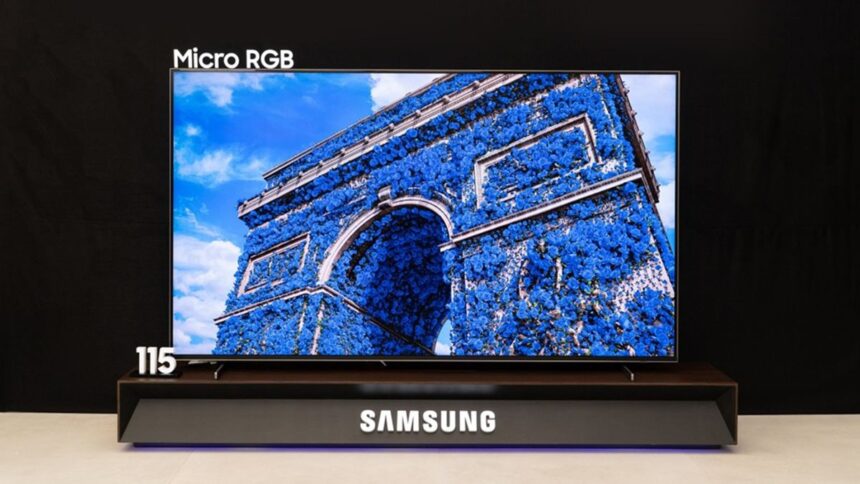
The TV market today is largely dominated by two display technologies, each with its own strengths. OLED panels are praised for their deep blacks and high contrast, while LCD-based TVs stand out for their brightness and longevity.
Micro RGB is emerging as a new alternative that aims to combine the best of both worlds, while avoiding many of the drawbacks found in current standards.
Although the name may sound similar to other display technologies, Micro RGB operates in a distinctly different manner-especially when compared to traditional Mini-LED televisions.
The evolution beyond Mini-LED
To understand what makes Micro RGB different, it is helpful to examine how TV backlighting works. Most LCD TVs today rely on white or blue LEDs placed behind the panel. These LEDs shine through colour filters to create red, green, and blue pixels on the screen. While effective, this process is inefficient, as a significant portion of the original light is lost during the filtering process.
Micro RGB changes this approach entirely. Instead of using white or blue light, it places microscopic red, green, and blue LEDs directly in the backlight itself. This means the light is already the correct colour before it reaches the screen, eliminating the need for heavy filtering.
The result is a more efficient system that delivers stronger colors and more accurate brightness. Because the light no longer needs to be filtered, colour saturation remains intact even in very bright scenes, improving overall image realism.
How Micro RGB differs from MicroLED
Despite the similar naming, Micro RGB and MicroLED are not the same technology.
MicroLED panels completely remove the liquid crystal layer found in LCD TVs. Each pixel becomes a self-emissive LED that turns on and off independently, similar in concept to OLED-but without organic materials. While impressive, MicroLED displays are extremely difficult and expensive to manufacture.
Micro RGB, on the other hand, retains the LCD structure. It improves the existing design rather than replacing it entirely. The innovation lies in the backlight, which gains precise color control without the complexity or cost of fully self-emissive pixels. This makes Micro RGB a more practical evolution of current LCD technology.
Brightness, colour volume, and contrast
One of the biggest weaknesses of many modern TVs is color washout at high brightness levels. As screens get brighter, colors often lose saturation. Micro RGB directly addresses this issue.
By emitting pure red, green, and blue light from the source, Micro RGB displays are designed to cover the full BT.2020 color space, a standard used in professional cinema. This allows for richer reds, purer greens, and consistent color intensity even in extremely bright HDR scenes.
Brightness is another major advantage. Thanks to its higher efficiency, Micro RGB TVs are expected to exceed 4,000 nits, making them especially well-suited for HDR content and significantly brighter than most OLED panels.
Contrast also benefits from improved backlight control. The system can dim or shut off extremely small zones behind the LCD layer, producing deeper blacks and minimising light bleed around bright objects.
Durability and long-term reliability
Another key benefit of Micro RGB is durability. Unlike OLED panels, which rely on organic compounds that degrade over time, Micro RGB uses inorganic LEDs. This eliminates the risk of permanent image retention, commonly known as burn-in, and helps extend the display’s lifespan.
A promising middle ground
Micro RGB represents a smart middle path in display technology. It preserves the strengths of LCD-brightness, durability, and scalability-while significantly improving colour accuracy, contrast, and efficiency.
By avoiding the manufacturing challenges of MicroLED and the longevity concerns of OLED, Micro RGB positions itself as a strong contender for the future of high-end televisions.
- What Is Manus AI
- What is Xbox Game Bar
- What Is a RAM Bandwidth Bottleneck
- What is PowerShell, and why is it used