In some situations, especially with a brand-new computer, you may want to remove the manufacturer’s pre-installed partitions. When Windows Disk Management refuses to delete them, DISKPART is often the solution.
DISKPART is a built-in system utility that gives you deeper, low-level control over your storage drives. Unlike Disk Management, it can bypass many of the restrictions placed on protected or OEM partitions. Using this tool, you can fully delete manufacturer-created partitions and take complete control of how your drive is organized.
By removing these partitions, you’re free to reformat the drive and create your own partition layout, rather than adhering to the factory configuration. DISKPART is especially useful when standard Windows tools fall short, offering the flexibility needed to start fresh and configure your storage exactly the way you want.
Delete default partitions
Hard drive makers often pre-partition USB drives to include an encryption option. This typically creates a small visible partition and a larger hidden, encrypted one. While convenient for some, other users may find this annoying or unnecessary. However, attempting to delete the partitions in Windows Disk Management fails, even with administrative rights.
This is where the DISKPART command-line tool can help. DISKPART comes with Windows and lets you reformat hard disks as needed.
To use DISKPART, open a PowerShell window or Command Prompt as administrator. Running with elevated rights is crucial for full disk access.
You can remove unwanted drive manufacturer partitions with the admin Command Prompt and the DISKPART tool. I’ll explain the steps next.
Important: Be sure to start as an administrator (right-click -> “Run as administrator”).
Delete all partitions with Diskpart.
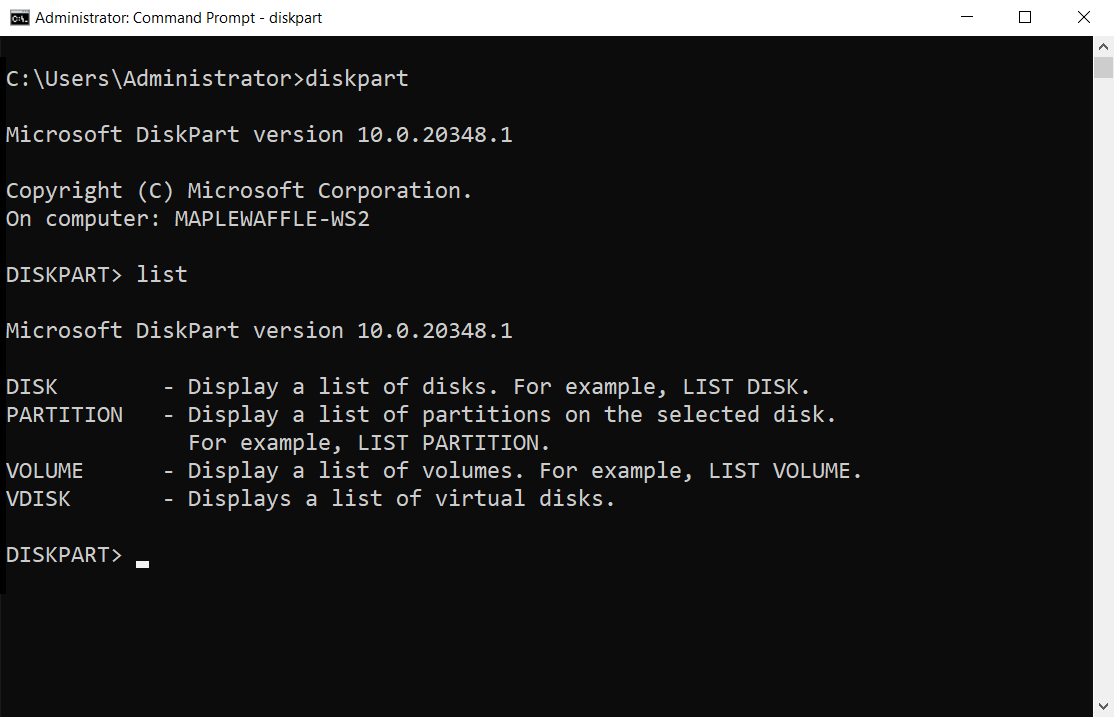
When you open Windows PowerShell, begin typing the “diskpart” command to launch the Diskpart program. This will display information about the Diskpart version and the computer’s name. To view all connected hard drives (both internal and external),
use the “list disk” command.
Be cautious and identify the specific data carrier you want to work with.
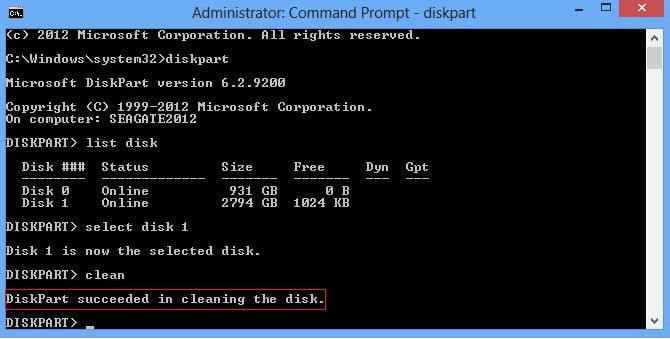
Now, use the “select disk 1” command to choose the hard drive you want to erase. Make sure to enter the correct number for your hard drive. To confirm your selection, use the “list disk” command; the corresponding line should now be marked with an asterisk.
To remove all partitions from the disk, enter the “clean” command. This action deletes all partitions and erases other information on the data carrier. Confirm the changes by using the “list disk” command.
After deleting partitions, you can initialize and reconfigure the disk. Use the Windows graphical interface – Disk Management (Windows key + X or diskmgmt. msc) – to reinitialize the deleted data carrier and partition it according to your preferences. If desired, you can continue using Diskpart for this process.
I created this guide because I frequently need to format a Laptop or PCs. I hope it helps someone else dealing with a similar task.
Delete pre-partitioned USB sticks?
Unfortunately, this approach doesn’t always work. If the manufacturer has written the configuration firmly into the firmware of a USB data carrier, there is no chance of removing the partitioning.